Selection with the Bitzer Software
At present, the Bitzer Software offers calculations with frequency inverter only for semi-hermetic compressors.
Step 1: Choosing the compressor
First choose the refrigerant, cooling capacity and operating points, and select "External FI". Then start the calculation by clicking on the button  . The software will then offer two suitable compressors in the range of the maximum operating frequency, each with its standard motor (Application range). If one of the compressors is chosen, the software indicates frequency, cooling capacity and current consumption (voltage):
. The software will then offer two suitable compressors in the range of the maximum operating frequency, each with its standard motor (Application range). If one of the compressors is chosen, the software indicates frequency, cooling capacity and current consumption (voltage):
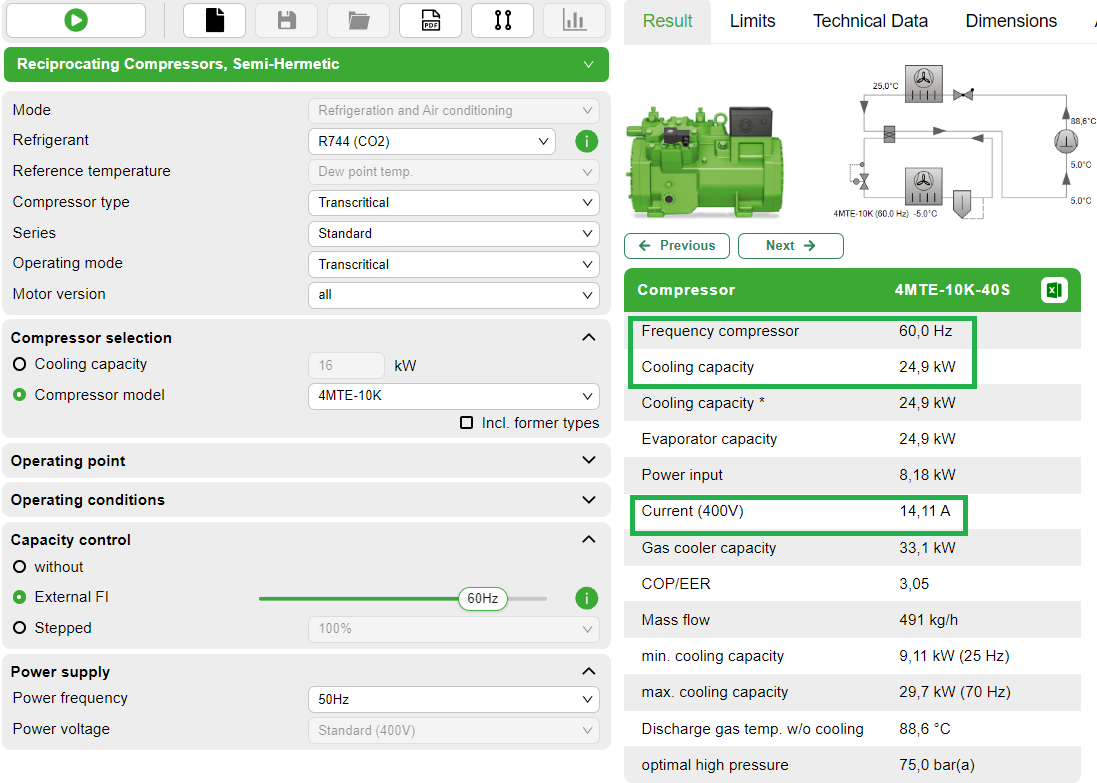
By gradually increasing the operating frequency (slider at "External FI"), the maximum operating frequency for the selected combination of compressor, refrigerant and operating point can be found. For operation above this frequency, a larger motor version (chosen in the menu "Compressor model") or a special voltage motor (Compressor motors) may be available. The calculation of special voltage motors, however, is not implemented in the Bitzer Software and available on request.
Step 2a: Selecting a Bitzer Varipack frequency inverter (if available)
Chosse the tab "Accessories" in the menu bar at the top.
The tab for the accessories module only becomes active after selecting a compressor.
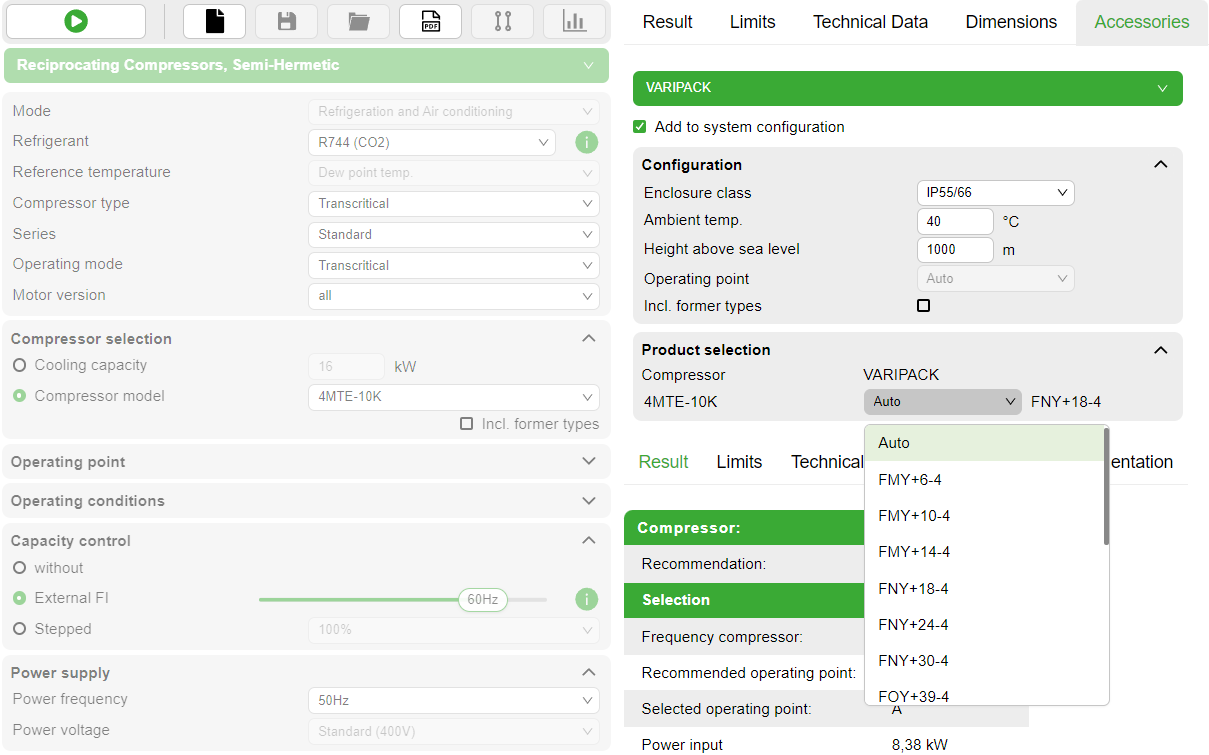
The appropriate frequency inverter can be chosen directly in the accessory module. Due to the modular design of the Varipack frequency inverters, a wide range of versions is available – flexible and matching the Bitzer compressors. For details see info button next to the slider at "External FI"  .
.
The starting characteristics of the compressors have been optimised for Varipack frequency inverters, tested for the different refrigerants, and the results are implemented in the Bitzer software. This ensures a safe compressor start with Varipacks under all conditions.
In addition, the Bitzer software visualises the resulting frequency limits of the currently selected combination of compressor, refrigerant, operating point and Varipack frequency inverter in the application limit:
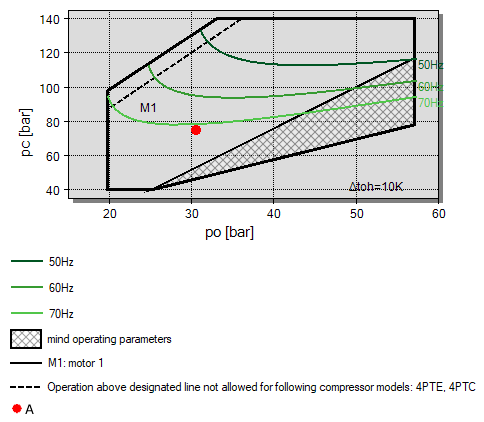
If less restrictions regarding the maximum possible frequency are desired, it may be possible to extend them by selecting a larger frequency inverter (unless the motor is the limiting factor):
For further details on the Varipack see Operating Instructions CB-110.
Step 2b: Selecting a frequency inverter of another manufacturer
- Allow at least 10% reserve for operating current
The frequency inverter must be able to continuously supply the operating current to the compressor under all expected operating conditions. At least 10% additional reserve should be planned for, e.g. to be able to compensate for undervoltage in the network. If the frequency inverter has limiter functions which limit the maximum frequency under such circumstances to ensure operational safety (such as the Bitzer Varipack), the reserve can possibly be selected smaller.
- Consider overload capacity for compressor start
Additionally, a compensation factor FC for the current during the compressor start must be allowed for. Since the torque of reciprocating compressors is not constant with the angle of rotation (the higher the number of cylinders, the more constant the torque), a greater starting torque is required for a smaller number of cylinders. The compensation factors are as follows:
- 2 cylinder compressors for R744: F = 3
- other 2 cylinder compressors: F = 2.0
- 4 cylinder compressors: F = 1.6
- 6 cylinder compressors: F = 1.5
- 8 cylinder compressors: F = 1.4
This factor is multiplied by the "Max. operating current" that the Bitzer software indicates for the respective motor in the tab "Technical data" (see figure below). This maximum current must be within the short-term overload capacity of the frequency inverter, otherwise a larger frequency inverter is necessary.
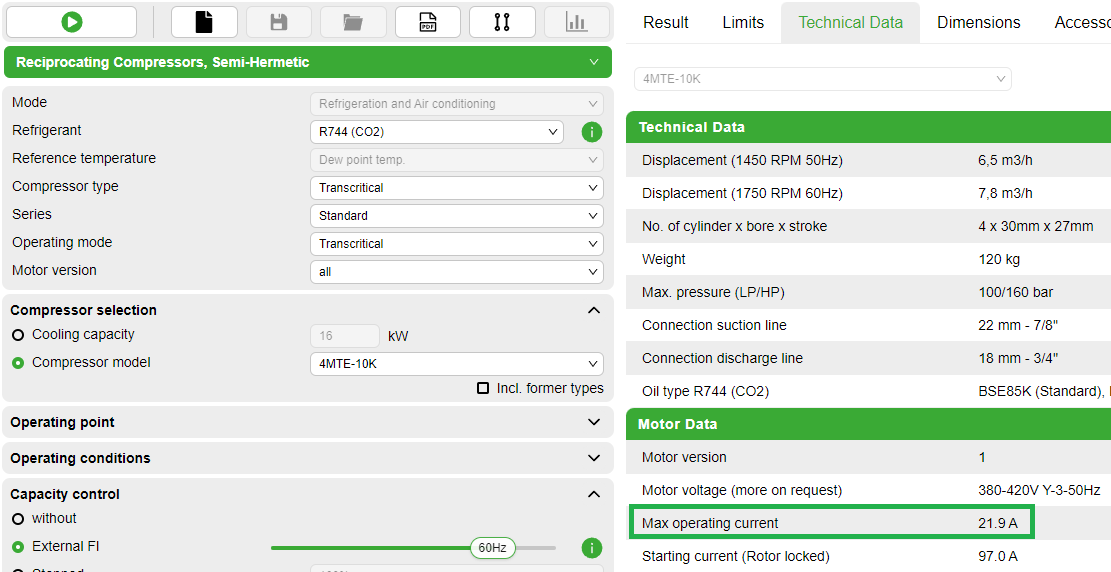
multiplied by the compressor-specific compensation factor (for 4 cylinder compressors: F = 1.6)
gives the necessary short-term overload capacity of the frequency inverter.
For Bitzer Varipack frequency inverters, this is already taken into account by design.