Extended greenhouse gas balance CFP on a refrigerant compressor
Taking a reciprocating compressor widely used in commercial refrigeration as an example, data for the greenhouse gas balance are presented. For this, the following most important impacts are evaluated:
- carbon dioxide emissions through electrical energy consumption during operation
- carbon dioxide equivalent of the refrigerant emissions over the life time
- carbon dioxide emissions through the material use
- carbon dioxide emissions through the energy use during production
For this balance, a series of assumptions had to be made.
Balance content definition and limitations
Material and energy consumption only for the compressor. Operation in a condensing unit with a mid sized condenser in a refrigeration system. Operating time 15 years. The material contents were determined, the production emissions taken from the environmental report and in the first stage divided by the total production numbers of the year. The emission data of the materials were taken from the material data base of the German environmental protection agency Umweltbundesamt (UBA).
This balance is derived from the TEWI balance, well known in refrigeration, although only a small amount of the refrigerant leakage can be attributed to the compressor. It thus differs from the emission balance for Directive 2022/2464/EU CSRD with regards to corporate sustainability reporting. The balance does, however, not contain the emissions from production of the refrigerant. For more complex substances like R1234yf (for the amount of refrigerant in this example) and depending on the data source, these emissions can even be higher than those from material and production of the compressor.
Conditions
Operation is calculated at nominal conditions for the determination of the seasonal energy performance ratio SEPR according to EN13215 for low temperature refrigeration LT at to -35°C and medium temperature refrigeration MT at to -10°C.
present | option | |
|---|---|---|
4 cylinder | 4NES-14Y | |
Refrigerant MT | R134a | R1234yf |
GWP refrigerant MT | 1430 | 4 |
Refrigerant LT | R404A | R454C |
GWP refrigerant LT | 3922 | 148 |
Conversion factor electric kg CO2/kWh | 0,401 | |
Load + temperature curve | EN13215 | |
System life time in a | 15 | |
Leak rate in %/a | 3 | |
Reclaim loss in % | 10 | |
Refrigerant charge | according to BITZER Software |
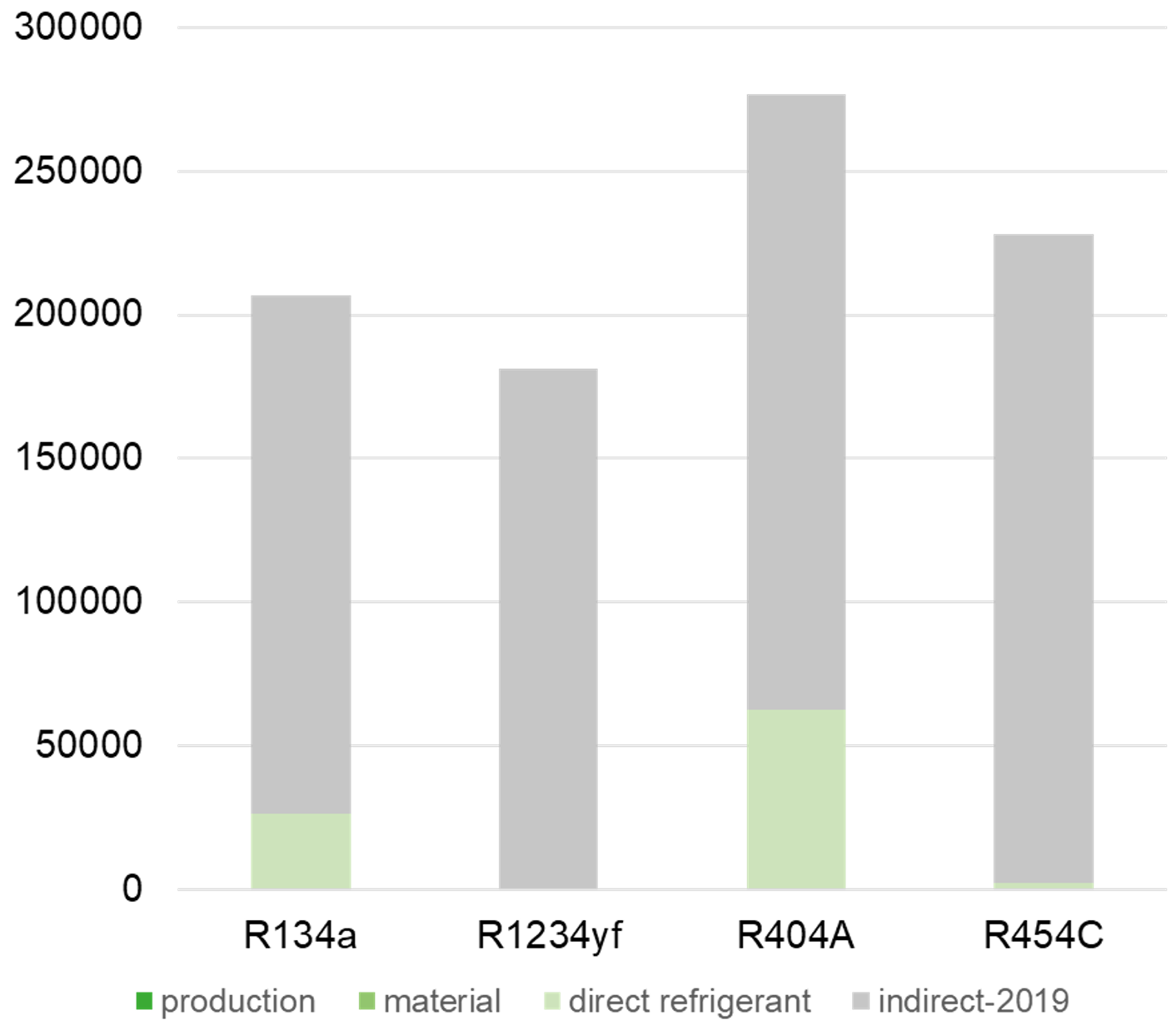
Analysis of the impact parts
In the total balance, the far largest part is connected to the energy consumption (in gray). For refrigerants with high global warming GWP, also this part is clearly visible in the total balance (in light green). This is the reason for typically using the TEWI balance in refrigeration which works with these two parts.
If the future brings electrical energy from sustainable sources only and the GWP of the used refrigerants decrease remarkably, the two major parts of the balance disappear.
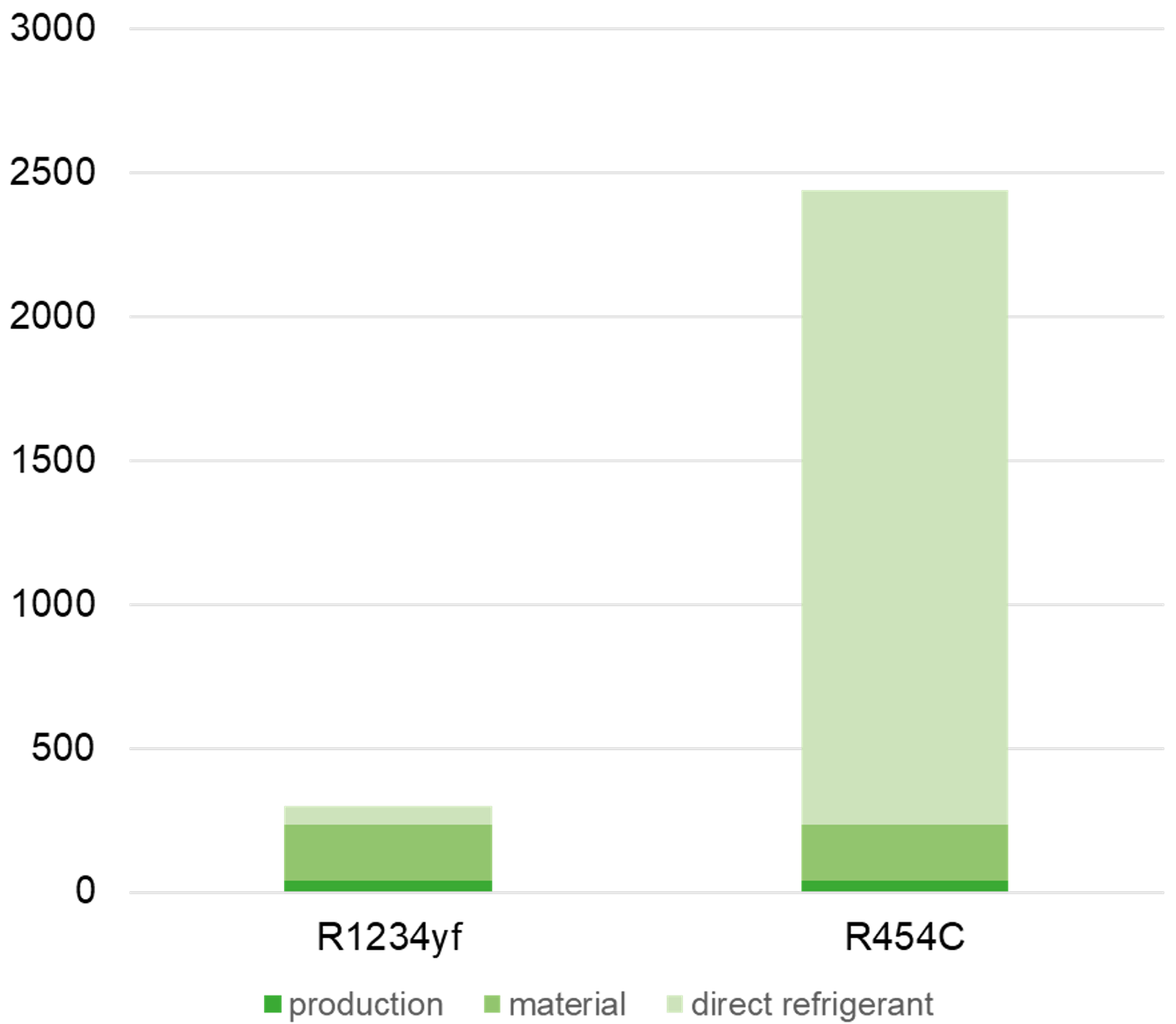
In the figure without the part of the energy consumption, even with a refrigerant with a global warming of GWP 148, like R454C, the part of the refrigerant emission is the largest. At GWP 4, like with R1234yf, the part of the refrigerant is smaller than that of the materials (in medium green).
The part of the production (in dark green) is clearly the smallest and should also even decrease in future, through the use of sustainable energy sources.
The next focus topic in eco balances will be on the materials. For compressors, this part is relatively small, also because of a high recycling rate of cast iron and copper. And even here, the use of energy from sustainable sources is possible to a wide extent. This, however, means for eco balances that the source location and the way of production of materials will become important in future. It cannot be expected that the production of materials world wide will be converted to sustainable energy sources within a few years. When balancing a complete refrigeration installation, the material part will be larger.
The most refrigeration, air conditioning and heat pump systems in the world are powered electrically. Through this, they are easy to convert to sustainable energy. The part of refrigerants with high global warming potential will be decreasing strongly within the next years in the EU and there are efficient refrigerants with low GWP. Because of these two points, the emission balance of refrigeration looks much better in future.